Recently, I discovered a fantastic automation tool called “Make,” which offers a 30-day trial with full access to all features. After the trial, you seamlessly transition to the free version, providing ample time to explore and determine if this tool is right for you.
I quickly realized that Make could be invaluable for automating the creation of content across platforms like TikTok, YouTube, Facebook, and X (formerly Twitter).
In this post, I’ll walk you through how I’m using Make to streamline the process of creating video game reviews for my YouTube channel. If you’re interested, you can check out the channel here: PXL Reviews on YouTube.
To get started with Make, visit make.com. Once you’ve activated your free trial, you’ll be greeted with a dashboard where you can monitor the performance of your “scenarios.” A scenario in Make is a set of visual instructions that dictate how tasks are automated, with each scenario comprising multiple “modules.” These modules are the actions Make performs, such as connecting to ChatGPT to ask a question or adding a row of data to a Google Sheet.
Here’s an example of a scenario I created to automate the production of content for my YouTube channel:
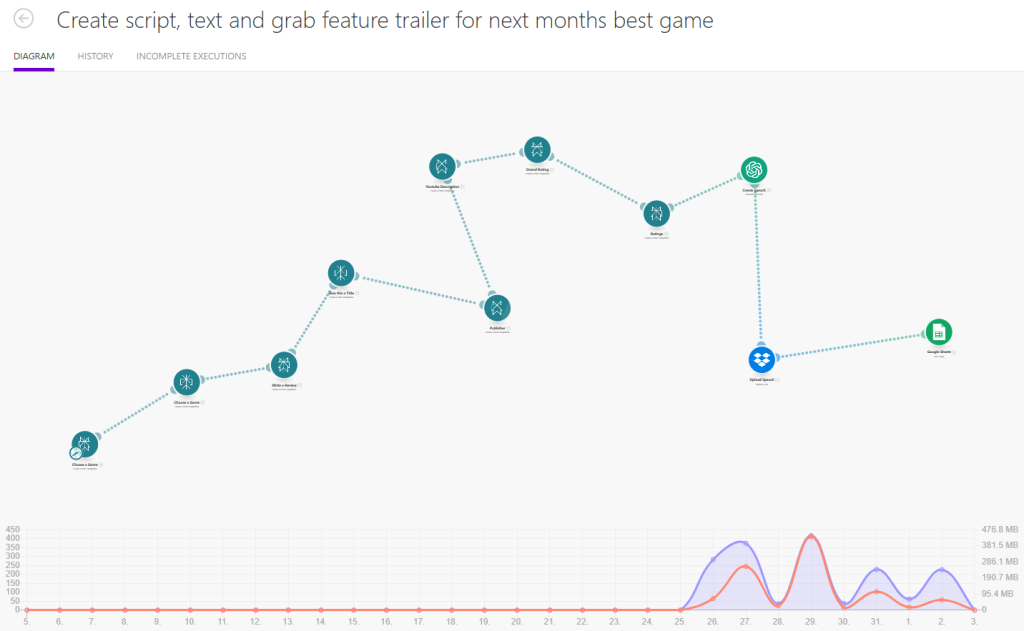
Breakdown
1. Pick a Genre
First, I connect to Perplexity and ask it to randomly select a video game genre. The prompt is simple: “Pick a genre of video game at random and give me the genre as a simple piece of text, with no explanation or other information. Ensure the text does not contain any characters other than letters & numbers.”
The result is then passed to the next module.
2. Choose a Game
Next, I ask Perplexity to provide the title and publisher of an upcoming video game in the selected genre. The prompt is: “Give me the title and publisher of a popular video game coming out soon in the {{28.choices[].message.content}} genre. Provide your answer in the format of the ‘title’ and the ‘publisher’ of the game. Do not provide any other text.”
This module uses the genre provided by the first module to generate the game title and publisher.
3. Write a Review
In this step, Perplexity is asked to write a review for the upcoming game: “You are a video game reviewer. Write a review on this upcoming game for 2025. {{20.choices[].message.content}}. The text must not exceed 4000 characters and must not contain any section headers.”
The review is generated based on the game chosen in the previous module.
4. Give this a Title
In this simple module, perplexity will provide the title of the game.
5. Publisher
Perplexity then returns the publisher of the game. The information from previous modules (title, publisher, genre) can be used later in the scenario for different purposes.
6. Youtube Description
This module generates a description for the YouTube video, encouraging viewers to like and subscribe.
7. Overall Rating
Here, I use Perplexity to provide an overall rating for the game based on the review. The prompt is: “Give me a one-word rating for this game, choose from either ‘bad,’ ‘needs work,’ ‘good,’ ‘average,’ ‘great,’ ‘fantastic,’ ‘outstanding,’ or ‘breathtaking.’ Do not include any other text other than the one-word rating. Here is the game review: {{21.choices[].message.content}}.”
8. Ratings
In this module perplexity provides a breakdown of key elements of the game and provides a score for each. “bsed on the information you have here: {{21.choices[].message.content}} provide numeric ratings from 1 to 5 (1 being bad, 5 outstanding) for each of the following: gameplay, graphics, sound, value. Do not provide any other text, just the area being rated and the numeric rating in the form of a table.”
9. Create Speech
This module calls upon chatgpt to use its text to speech engine tts-1-hd model to convert the review created earlier into a spoken mp3 file.
10. Upload Speech
Here we use dropbox to save the mp3 file created in the previous module.
11. Google Sheets
In this final module we add a row to a google spreadsheet and record the above data.
title, publisher, genre, ratings, overall rating, youtube description, transcript
Once all these modules run, the scenario is complete. At this stage, I prefer to have some human involvement to ensure quality before uploading the content to my YouTube channel. This helps avoid uploading subpar content and risking subscriber loss.
With the data saved to a spreadsheet and the MP3 file ready, I move to the next step. Initially, I used a tool called “Apify” to search YouTube for appropriate game trailers, download them, and upload them to Canva. However, Apify can be costly, and the video quality isn’t always reliable. Instead, I wrote a PowerShell script to search YouTube for relevant videos.
# YouTube Search Scraper Script - John Allison 2024
function Search-YouTube {
param (
[string]$query,
[int]$maxResults = 10
)
# Encode the search query for URL
$encodedQuery = [uri]::EscapeDataString($query)
$url = "https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=$encodedQuery"
try {
# Send a GET request to the YouTube search page
$response = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $url -UseBasicParsing
# Extract the JSON data containing video information
$jsonRegex = 'var ytInitialData = ({.*?});'
$jsonMatch = [regex]::Match($response.Content, $jsonRegex)
if (-not $jsonMatch.Success) {
Write-Error "Could not find video data in the response."
return $null
}
$jsonContent = $jsonMatch.Groups[1].Value
$videoData = $jsonContent | ConvertFrom-Json
$videos = @()
$videoRenderers = $videoData.contents.twoColumnSearchResultsRenderer.primaryContents.sectionListRenderer.contents[0].itemSectionRenderer.contents |
Where-Object { $_.videoRenderer }
foreach ($renderer in $videoRenderers) {
if ($videos.Count -ge $maxResults) {
break
}
$videoInfo = $renderer.videoRenderer
$videos += [PSCustomObject]@{
Title = $videoInfo.title.runs[0].text
URL = "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=$($videoInfo.videoId)"
}
}
return $videos
}
catch {
Write-Error "An error occurred: $_"
return $null
}
}
# Example usage
$searchQuery = Read-Host "Enter your YouTube search query"
$searchQuery="official Trailer "+$searchquery
$results = Search-YouTube -query $searchQueryThis script returns 10 potential videos which can be downloaded and used.
Next I have another script which downloads a video from youtube. This script uses an open source tool called yt-dlp. Once you download this tool, place a copy somewhere accessible like c:\windows\system32
# Function to check if yt-dlp is installed
function Check-YtDlp {
$ytDlp = Get-Command yt-dlp -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
if ($null -eq $ytDlp) {
Write-Host "yt-dlp is not found in PATH. Here are some troubleshooting steps:"
Write-Host "1. Ensure yt-dlp.exe is downloaded and placed in a known directory."
Write-Host "2. Add that directory to your system's PATH."
Write-Host "3. Restart PowerShell and try again."
Write-Host "Current PATH:"
$env:Path -split ';' | ForEach-Object { Write-Host $_ }
exit
}
Write-Host "yt-dlp found at: $($ytDlp.Source)"
}
# Function to download YouTube video
function Download-YoutubeVideo {
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]$Url,
[string]$OutputPath = "c:\users\jwpa\Dropbox\Video Games\%(title)s.%(ext)s"
)
try {
Write-Host "Downloading video from: $Url"
yt-dlp -f "bestvideo[ext=mp4]+bestaudio[ext=m4a]/best[ext=mp4]/best" -o $OutputPath $Url --write-thumbnail
Write-Host "Download completed successfully."
}
catch {
Write-Host "An error occurred while downloading the video: $_"
}
}
# Main script
Check-YtDlp
$videoUrl = Read-Host "Enter the YouTube video URL"
Download-YoutubeVideo -Url $videoUrl
Finally, we have everything we need to create a video review of an upcoming game. To pull this all together I use canva, create a new design set to your chosen medium youtube, tiktok, etc. Upload your mp3 file and your video (be prepared to loop the video a couple of times as they tend to be much shorter than the mp3 file). And VOILA you have the basics done, you should look at opening/closing screens, and maybe add in the ratings to the video.
Conclusion
This example highlights the tremendous potential of Make as a versatile automation tool that can significantly streamline your workflow, especially when integrated with AI tools. By connecting various external resources and applications, Make allows you to automate complex tasks that would otherwise require significant manual effort and time.
In the case of creating video game reviews for a YouTube channel, Make not only simplifies the process but also enhances it by ensuring consistency and accuracy. The ability to automate the selection of a video game genre, the identification of upcoming titles, the generation of reviews, and the compilation of related content demonstrates how Make can be leveraged to produce high-quality content at scale. Each step in the process—from gathering data to generating text, creating audio, and finally uploading content—is seamlessly integrated, reducing the possibility of human error and freeing up valuable time for creative work.
Moreover, Make’s flexibility allows you to customize scenarios to suit your specific needs. Whether you’re managing a YouTube channel, running a social media campaign, or handling any other content-driven task, Make can adapt to your requirements. The inclusion of loops, conditions, and routes within your scenarios adds a layer of sophistication that can handle even the most intricate workflows. This adaptability ensures that the automation you build is not only effective but also scalable as your needs evolve.
The power of Make is further amplified when combined with AI tools like Perplexity and ChatGPT. By harnessing AI, you can automate tasks that require a degree of creativity and critical thinking, such as writing reviews or generating video titles. This integration between Make and AI opens up new possibilities for content creation and management, enabling you to produce content that is both relevant and engaging with minimal manual intervention.
While automation can handle many tasks, it’s important to recognize the value of human oversight. Automated systems are incredibly powerful, but they are not infallible. By reviewing and refining the output before publishing, you can maintain a high standard of quality, ensuring that your content resonates with your audience and retains their trust.
In summary, Make.com is an incredibly powerful tool that, when combined with AI and other automation tools, can revolutionize the way you create and manage content. Whether you’re a content creator, marketer, or business owner, Make offers a user-friendly platform that can help you automate repetitive tasks, enhance productivity, and focus more on the creative aspects of your work. As you continue to explore and refine your use of Make, you’ll likely discover even more ways it can transform your workflow, making it an indispensable part of your toolkit.